Many continuum models have been derived in recent years which describe the self-assembly of industrially utilisable crystalline films to a level of detail that allows qualitative comparisons with experiments. For thin-film problems, where the characteristic length scales in vertical and horizontal directions differ significantly, the governing surface diffusion equations can be reduced to simpler PDEs by making use of asymptotic expansions. Many mathematical problems and solutions emerge from such new evolution equations and many of them remind of Cahn-Hilliard type equations. The surface diffusion models are of high, of fourth or even sixth, order.
We present the modeling, model reduction and simulation results for heteroepitaxial growth as for Ge/Si quantum dot self-assembly. The numerical methods we are using are based on trigonometric interpolation. These kind of pseudospectral methods seem very well suited for simulating the coarsening of large quantum dot arrays. When the anisotropy of the growing crystalline film is strong, it might become necessary to add a corner regularisation to the model. Then the transition region between neighboring facets is still smooth, but its scale is rather small. In this case it might be useful to think about an adaptive extension of the existing method.
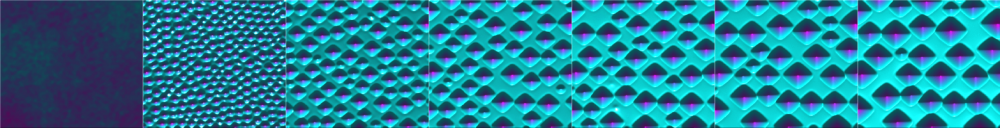
Figure 1: Ostwald ripening process of quantum dots depicted at consecutive time points. One fourth of the whole, periodic, simulated domain is shown.
Joint work with Peter Evans and Barbara Wagner

