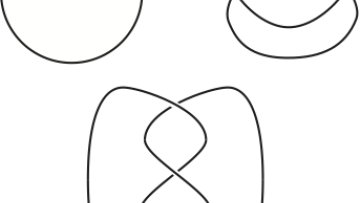
It is an intriguing fact that the 3-dimensional world in which we live is, from a mathematical point of view, rather special. Dimension 3 is very different from dimension 4 and these both have very different theories from that of dimensions 5 and above. The study of space in dimensions 2, 3 and 4 is the field of low-dimensional topology, the research area of Oxford Mathematician Marc Lackenby.
Oxford Mathematician Nick Trefethen was recently awarded the George Pólya Prize for Mathematical Exposition by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) "for the exceptionally well-expressed accumulated insights found in his books, papers, essays, and talks." Here Nick&n
As part of our series of research articles deliberately focusing on the rigour and intricacies of mathematics and its problems, Oxford Mathematician Nikolay Nikolov discusses his research in to Sofic Groups.
16:00
Existence of metrics maximizing the first eigenvalue on closed surfaces
Abstract
We prove that for closed surfaces of fixed topological type, orientable or non-orientable, there exists a unit volume metric, smooth away from finitely many conical singularities, that
maximizes the first eigenvalue of the Laplace operator among all unit volume metrics. The key ingredient are several monotonicity results, which have partially been conjectured to hold before. This
is joint work with Henrik Matthiesen.
Estimates of the distance to the set of divergence free fields and applications to analysis of incompressible viscous flow problems
Abstract
We discuss mathematical questions that play a fundamental role in quantitative analysis of incompressible viscous fluids and other incompressible media. Reliable verification of the quality of approximate solutions requires explicit and computable estimates of the distance to the corresponding generalized solution. In the context of this problem, one of the most essential questions is how to estimate the distance (measured in terms of the gradient norm) to the set of divergence free fields. It is closely related to the so-called inf-sup (LBB) condition or stability lemma for the Stokes problem and requires estimates of the LBB constant. We discuss methods of getting computable bounds of the constant and espective estimates of the distance to exact solutions of the Stokes, generalized Oseen, and Navier-Stokes problems.
Multiscale simulation of slow-fast high-dimensional stochastic processes: methods and applications
Abstract
We present a framework for the design, analysis and application of computational multiscale methods for slow-fast high-dimensional stochastic processes. We call these processes "microscopic'', and assume existence of an approximate "macroscopic'' model that captures the slow behaviour of a selected set of macroscopic state variables. The methodology combines short bursts of microscopic simulation with extrapolation at the macroscopic level. The methodology requires the careful study of a few key algorithmic ingredients. First, we need to properly initialise the microscopic system, based on a given macroscopic state and (possibly) a prior microscopic state that contains additional information about the system. Second, we need to control the variance of the noise that originates from the microscopic Monte Carlo simulation. Third, we need to analyse stability of the extrapolation step. We will discuss these aspects on two types of model problems -- scale-separated SDEs and kinetic equations -- and show the efficacity of the resulting methods in diverse applications, ranging from tumor growth to fusion energy.