THE SEARCH FOR TRANSIENT ASTROPHYSICAL NEUTRINO EMISSION WITH ICECUBE-DEEPCORE
Aartsen, M
Abraham, K
Ackermann, M
Adams, J
Aguilar, J
Ahlers, M
Ahrens, M
Altmann, D
Anderson, T
Ansseau, I
Archinger, M
Arguelles, C
Arlen, T
Auffenberg, J
Bai, X
Barwick, S
Baum, V
Bay, R
Beatty, J
Becker Tjus, J
Becker, K
Beiser, E
BenZvi, S
Berghaus, P
Berley, D
Bernardini, E
Bernhard, A
Besson, D
Binder, G
Bindig, D
Bissok, M
Blaufuss, E
Blumenthal, J
Boersma, D
Bohm, C
Börner, M
Bos, F
Bose, D
Böser, S
Botner, O
Braun, J
Brayeur, L
Bretz, H
Buzinsky, N
Casey, J
Casier, M
Cheung, E
Chirkin, D
Christov, A
Clark, K
Astrophysical Journal
issue 2
(10 Jan 2016)
An all-sky search for three flavors of neutrinos from gamma-ray bursts with the IceCube Neutrino Observatory
Sarkar, S
Astrophysical Journal
volume 824
issue 2
115
(01 Jun 2016)
Search for features in the spectrum of primordial perturbations using Planck and other datasets
Hunt, P
Sarkar, S
Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics
volume 2015
issue 12
052-052
(01 Dec 2015)
Mon, 15 Feb 2016
14:15
14:15
L4
Generalized Kähler structures from a holomorphic Poisson viewpoint
Marco Gualtieri
(Toronto)
Abstract
After reviewing the main results relating holomorphic Poisson geometry to generalized Kahler structures, I will explain some recent progress in deforming generalized Kahler structures. I will also describe a new way to view generalized kahler geometry purely in terms of Poisson structures.
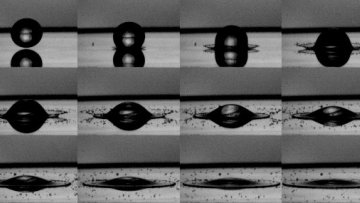
Understanding how droplets impact surfaces is important for a huge range of different applications. These range from spray painting, inkjet printing, fertiliser application and rainfall to crime-scene blood-splatter analysis and hygiene situations (men’s urinals being a familiar example). High speed movies show that when droplets hit surfaces fast enough, they often splash, emitting a corona of new, tiny droplets on impact.
Thu, 28 Jan 2016
11:00
11:00
C5
Not having rational roots is diophantine."
Philip Dittmann
(Oxford)
Abstract
"We give a diophantine criterion for a polynomial with rational coefficients not to have any
rational zero, i.e. an existential formula in terms of the coefficients expressing this property. This can be seen as a kind of restricted
model-completeness for Q and answers a question of Koenigsmann."