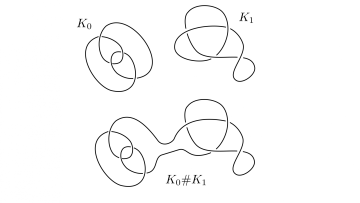
Knots are isotopy classes of smooth embeddings of $S^1$ in to $S^3$. Intuitively a knot can be thought of as an elastic closed curve in space, that can be deformed without tearing. Oxford Mathematician Daniele Celoria explains.
"Knots are ubiquitous in the study of the topological and geometrical properties of manifolds with dimension $3$ and $4$. This is due to the fact that they can be used to prescribe the attachment instructions for the "building blocks" of these spaces, through a process known as surgery.
Talks by Dphil students
Abstract
Tanut Treetanthiploet
---------------------
Exploration vs Exploitation under Statistical Uncertainty
The exploration vs Exploitation trade-off can be quantified and studied through the notion of statistical uncertainty using the theory of nonlinear expectations. The dynamic allocation problem of multi-armed bandits will be discussed. In the case of a finite state space in discrete time, we can describe the value function in terms of the solution to a discrete BSDE and obtain a similar notion to the Bellman equation. We also give an approximation scheme to evaluate decisions in the simple setting.
Julien Vaes
-----------
Optimal Execution Strategy Under Price and Volume Uncertainty
In the seminal paper on optimal execution of portfolio transactions, Almgren and Chriss define the optimal trading strategy to liquidate a fixed volume of a single security under price uncertainty. Yet there exist situations, such as in the power market, in which the volume to be traded can only be estimated and becomes more accurate when approaching a specified delivery time. To meet the need of efficient strategies in these situations, we have developed a model that accounts for volume uncertainty and show that a risk-averse trader has benefit in delaying their trades. We show that the optimal strategy is a trade-off between early and late trades to balance risk associated to both price and volume. With the incorporation of a risk term for the volume to trade, the static optimal strategies obtained with our model avoid the explosion in the algorithmic complexity associated to dynamic programming solutions while yielding to competitive performance.
Strategic Fire-Sales and Price-Mediated Contagion in the Banking System
Abstract
We consider a price-mediated contagion framework in which each bank, after an exogenous shock, may have to sell assets in order to comply with regulatory constraints. Interaction between banks takes place only through price impact. We characterize the equilibrium of the strategic deleveraging problem and we calibrate our model to publicly-available data, the US banks that were part of the 2015 regulatory stress-tests. We then consider a more sophisticated model in which each bank is exposed to two risky assets (marketable and not marketable) and is only able to sell the marketable asset. We calibrate our model using the six banks with significant trading operations and we show that, depending on the price impact, the contagion of failures may be significant. Our results may be used to refine current stress testing frameworks by incorporating potential contagion mechanisms between banks. This is joint work with Yann Braouezec.
Mean-Field Games with Differing Beliefs for Algorithmic Trading
Abstract
Even when confronted with the same data, agents often disagree on a model of the real-world. Here, we address the question of how interacting heterogenous agents, who disagree on what model the real-world follows, optimize their trading actions. The market has latent factors that drive prices, and agents account for the permanent impact they have on prices. This leads to a large stochastic game, where each agents' performance criteria is computed under a different probability measure. We analyse the mean-field game (MFG) limit of the stochastic game and show that the Nash equilibria is given by the solution to a non-standard vector-valued forward-backward stochastic differential equation. Under some mild assumptions, we construct the solution in terms of expectations of the filtered states. We prove the MFG strategy forms an \epsilon-Nash equilibrium for the finite player game. Lastly, we present a least-squares Monte Carlo based algorithm for computing the optimal control and illustrate the results through simulation in market where agents disagree on the model.
[ joint work with Philippe Casgrain, U. Toronto ]
Zero-sum stopping games with asymmetric information
Abstract
We study the value of a zero-sum stopping game in which the terminal payoff function depends on the underlying process and on an additional randomness (with finitely many states) which is known to one player but unknown to the other. Such asymmetry of information arises naturally in insider trading when one of the counterparties knows an announcement before it is publicly released, e.g., central bank's interest rates decision or company earnings/business plans. In the context of game options this splits the pricing problem into the phase before announcement (asymmetric information) and after announcement (full information); the value of the latter exists and forms the terminal payoff of the asymmetric phase.
The above game does not have a value if both players use pure stopping times as the informed player's actions would reveal too much of his excess knowledge. The informed player manages the trade-off between releasing information and stopping optimally employing randomised stopping times. We reformulate the stopping game as a zero-sum game between a stopper (the uninformed player) and a singular controller (the informed player). We prove existence of the value of the latter game for a large class of underlying strong Markov processes including multi-variate diffusions and Feller processes. The main tools are approximations by smooth singular controls and by discrete-time games.
Static vs Adaptive Strategies for Optimal Execution with Signals
We consider an optimal execution problem in which a trader is looking at a short-term price predictive signal while trading. In the case where the trader is creating an instantaneous market impact, we show that transactions costs resulting from the optimal adaptive strategy are substantially lower than the corresponding costs of the optimal static strategy. Later, we investigate the case where the trader is creating transient market impact. We show that strategies in which the trader is observing the signal a number of times during the trading period, can dramatically reduce the transaction costs and improve the performance of the optimal static strategy. These results answer a question which was raised by Brigo and Piat [1], by analyzing two cases where adaptive strategies can improve the performance of the execution. This is joint work with Claudio Bellani, Damiano Brigo and Alex Done.