Have you ever picked up a glass to find that the coaster it was resting on remains stuck to the bottom? If so, then you have experienced the ability of fluid to stick two surfaces together. When the bottom of the glass is wetted, for example by accidentally spilling a drink, then this fluid can fill the gap between the glass and coaster. The surface tension of the liquid then provides a pulling force on the coaster that keeps it attached to the glass.
From nanophotonics to aeroplanes, there are many applications that involve scattering in unbounded domains. Typically, one is interested in situations and geometries where there are no known analytical solutions and one has to resort to numerical algorithms to solve the problem using a computer. Such numerical algorithms should give physically meaningful solutions and hopefully obtain them with the minimal computational cost and time.
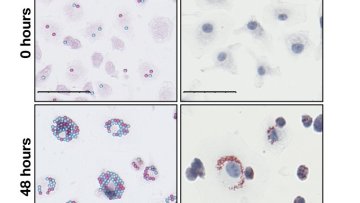
Certain inflammatory and infectious diseases, including atherosclerosis and tuberculosis, are caused by the accumulation inside immune cells of harmful substances, such as lipids and bacteria. A multidisciplinary study published in Proceedings B of the Royal Society, by researchers from the Universities of Oxford and Sydney, has shown how cell cannibalism contributes to this process.